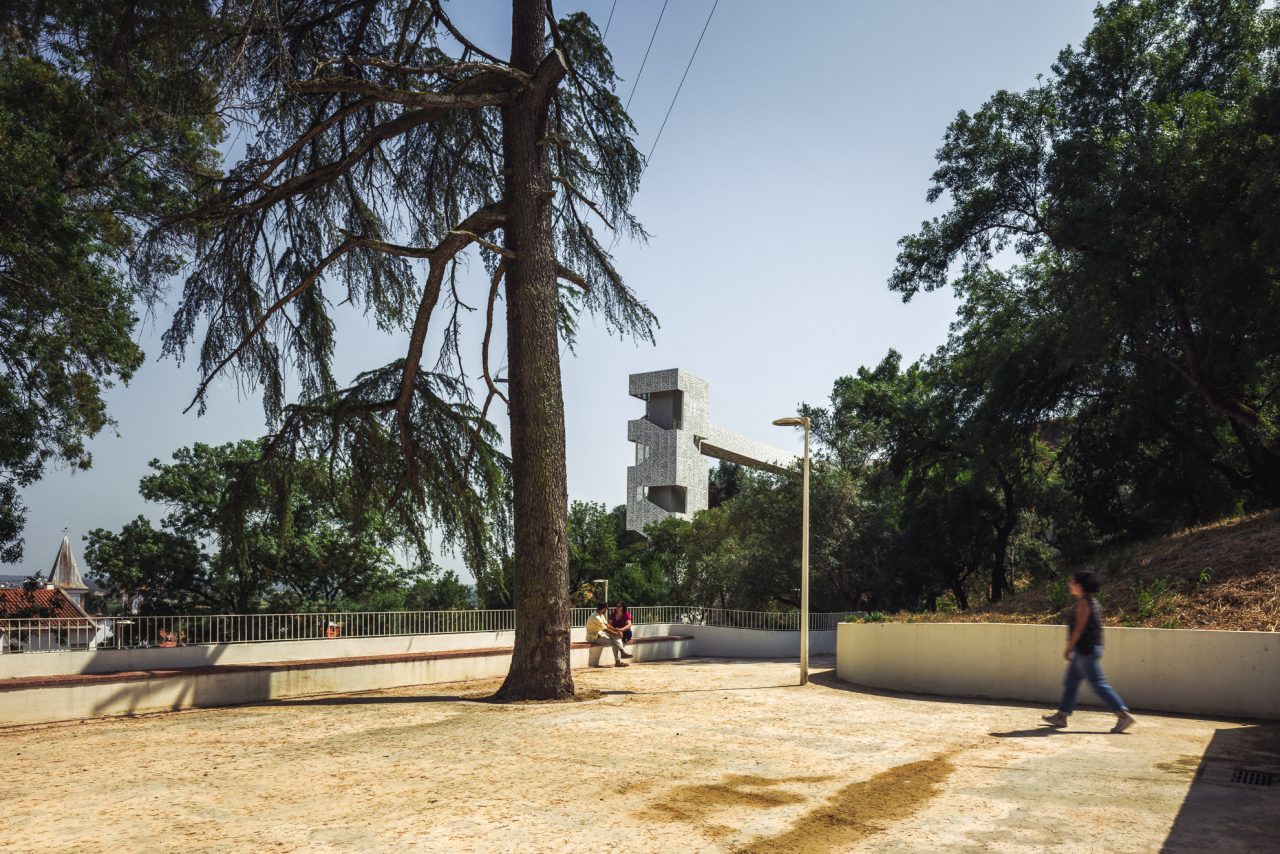
Similar to the initiative that led to the improvement of Calçadinha in 1978, with the aim of making the town more inclusive and accessible to all citizens, Coruche Municipality decided to promote an urban mobility project that would create a universal connection between the riverside area and the upper part of the town, while also improving the conditions for crossing the Calçadinha staircase through its rehabilitation.

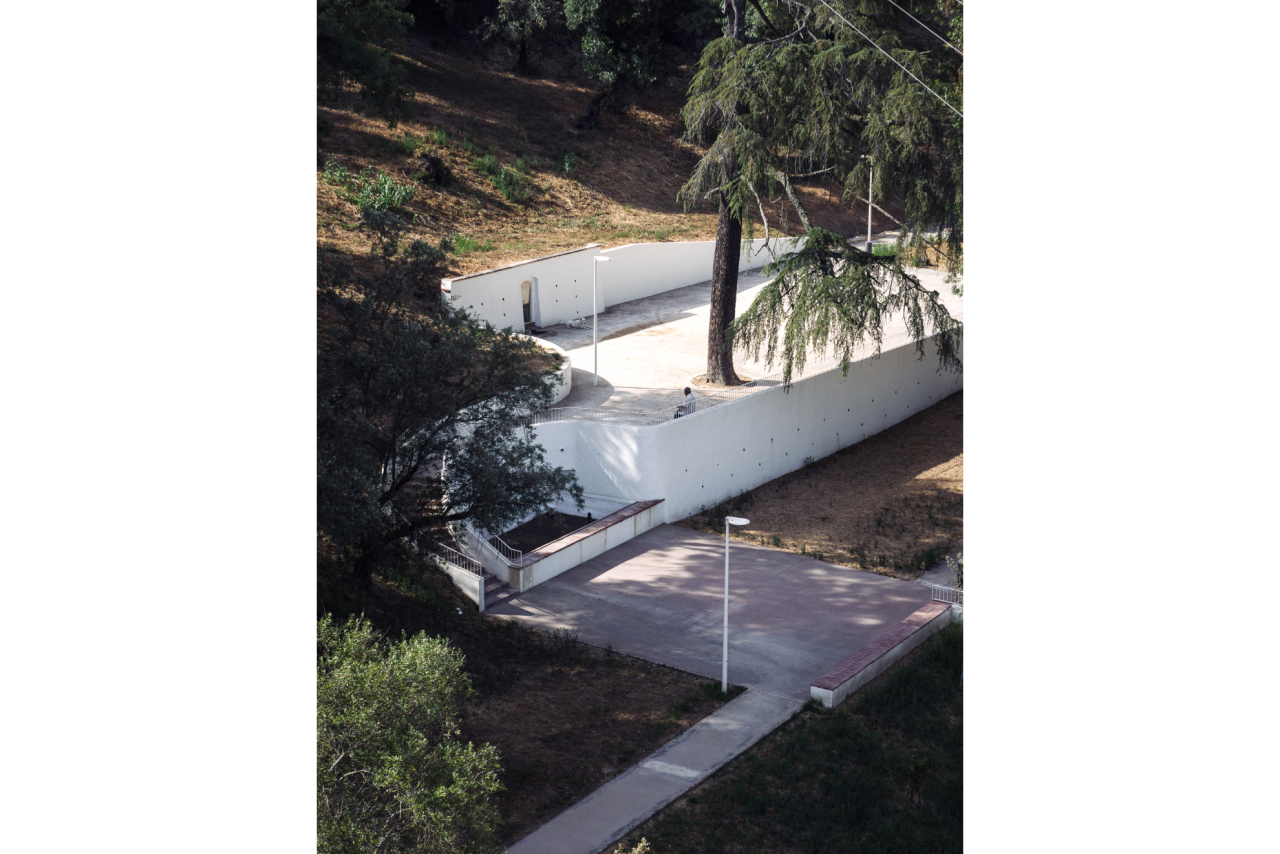
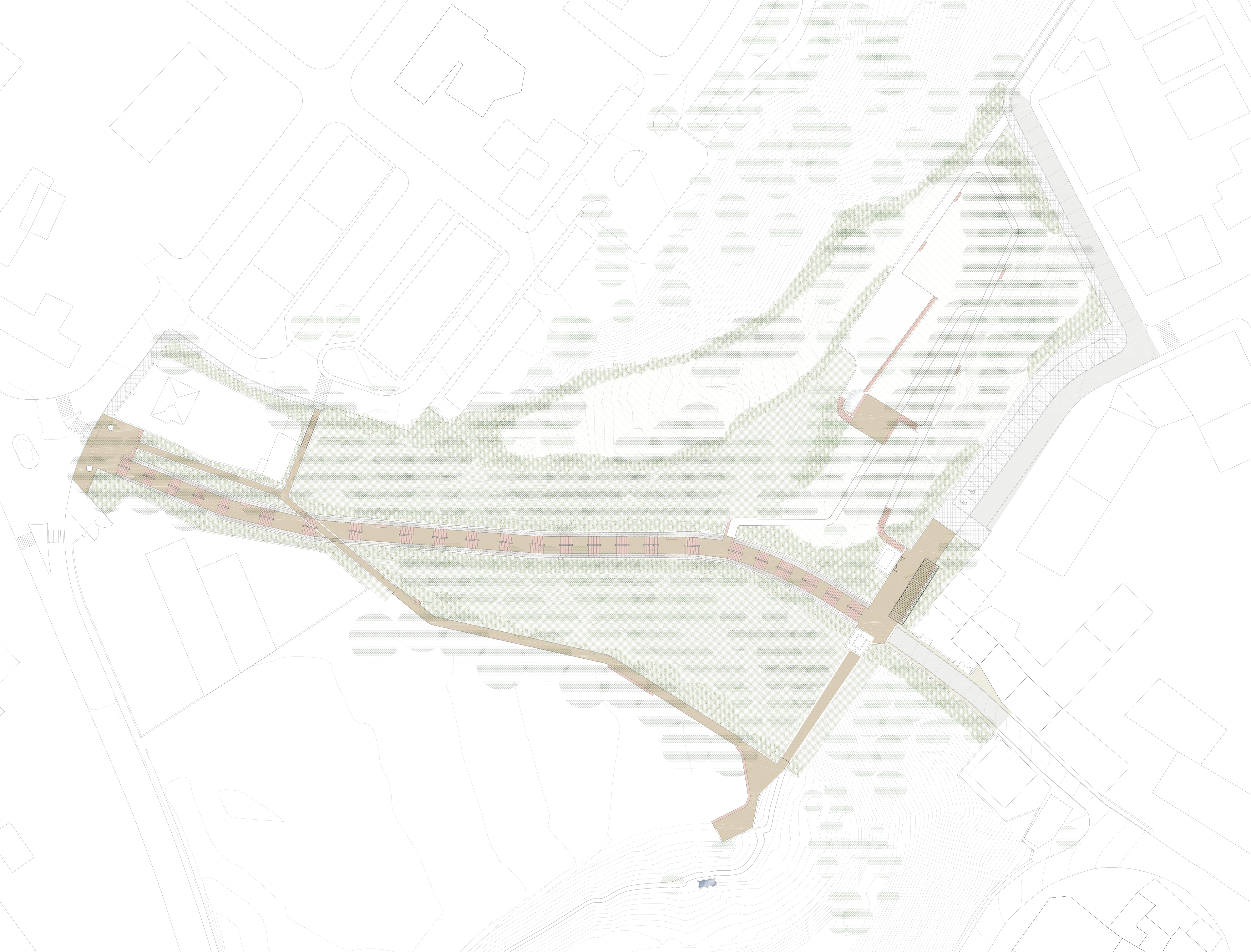
Calçadinha requalification project in Coruche involves redesigning the pedestrian circulation network, including the creation of a universally accessible route, defining a vegetation management strategy for the northern and southern slopes of Calçadinha, and creating public spaces for community enjoyment in an important transitional area that links the riverside zone to the upper part of the town.
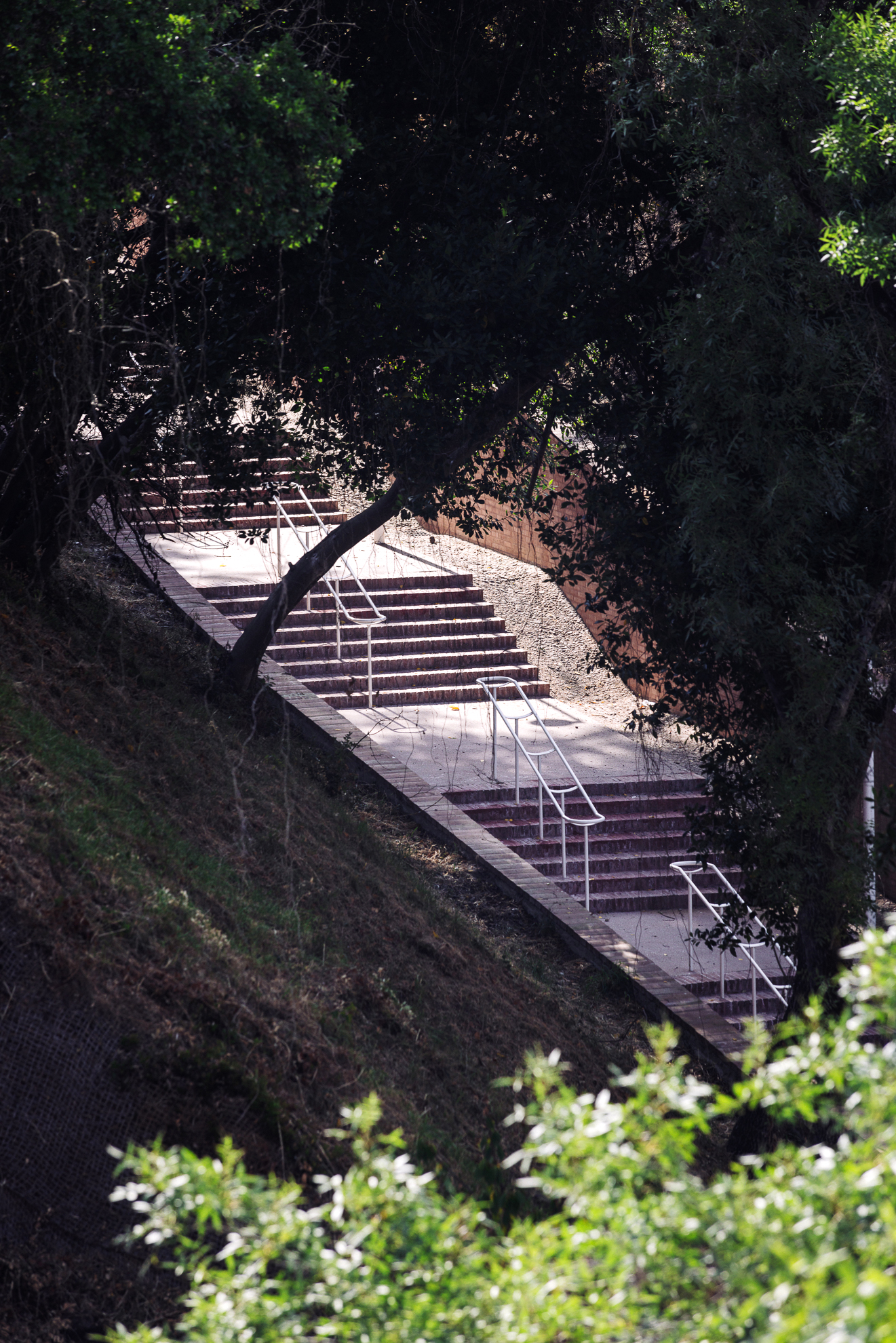
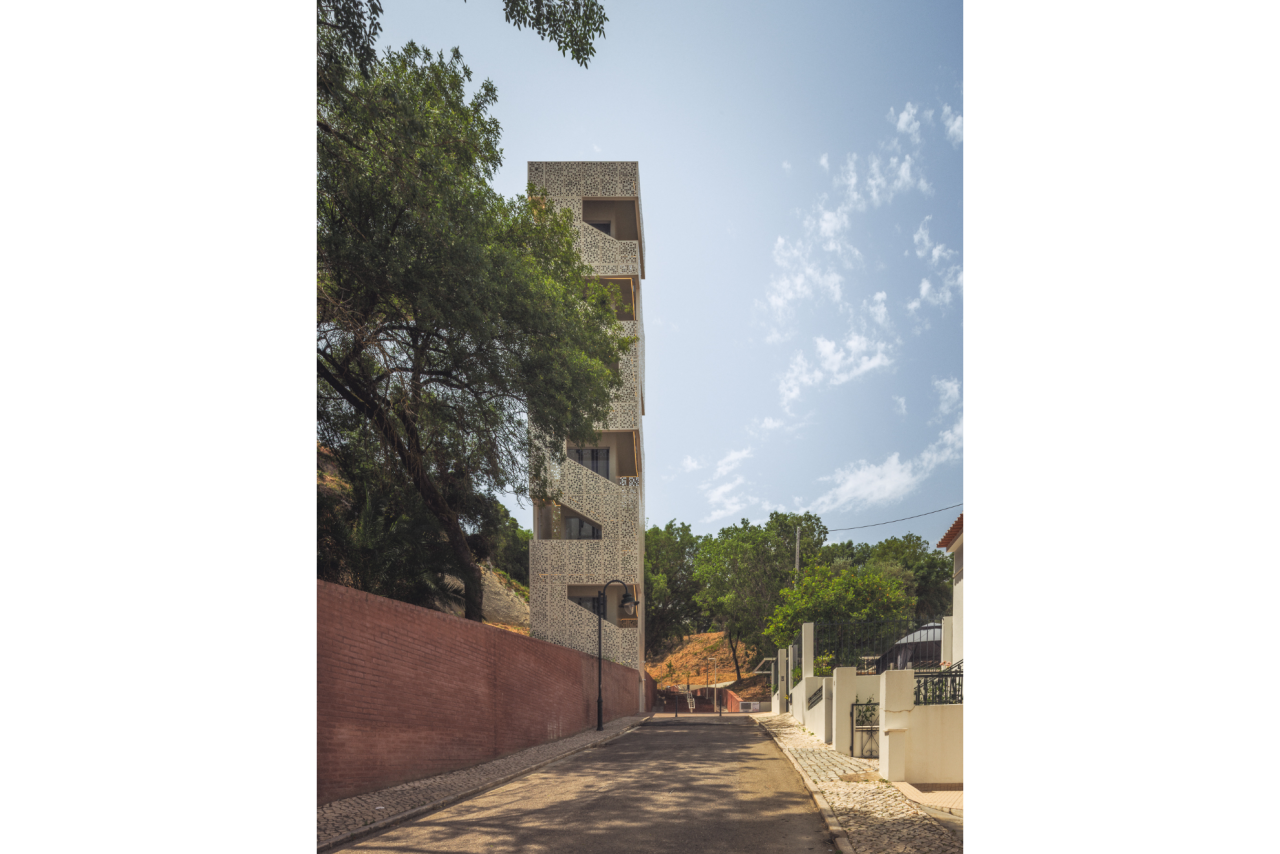
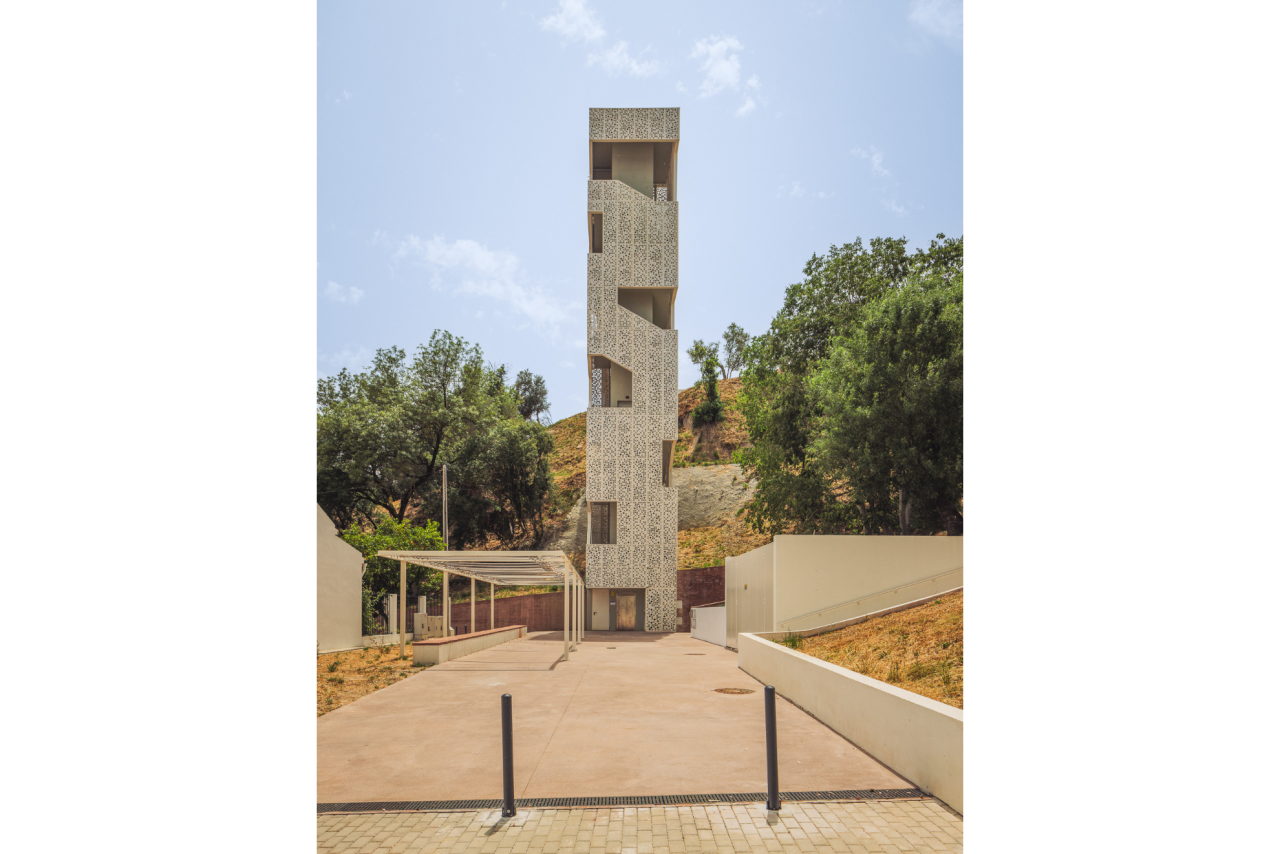
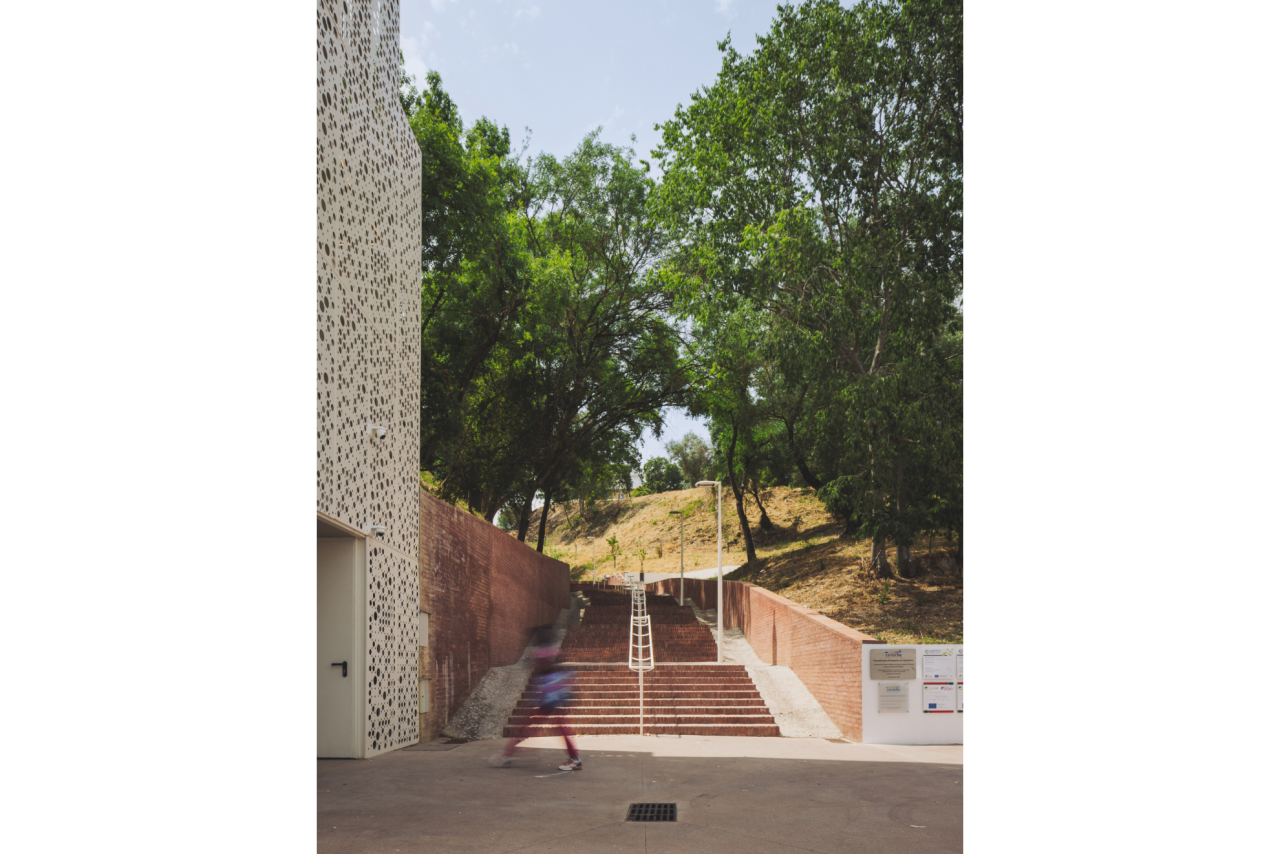
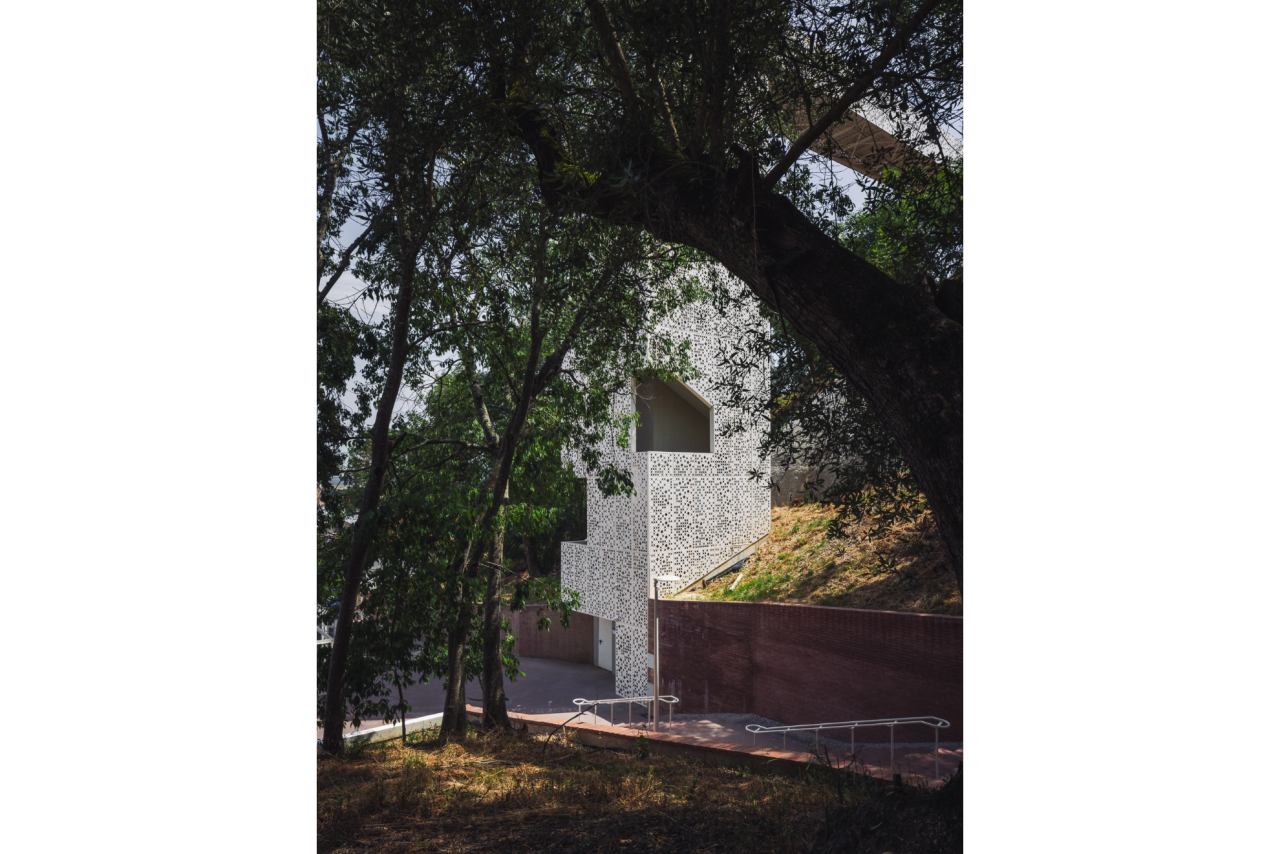
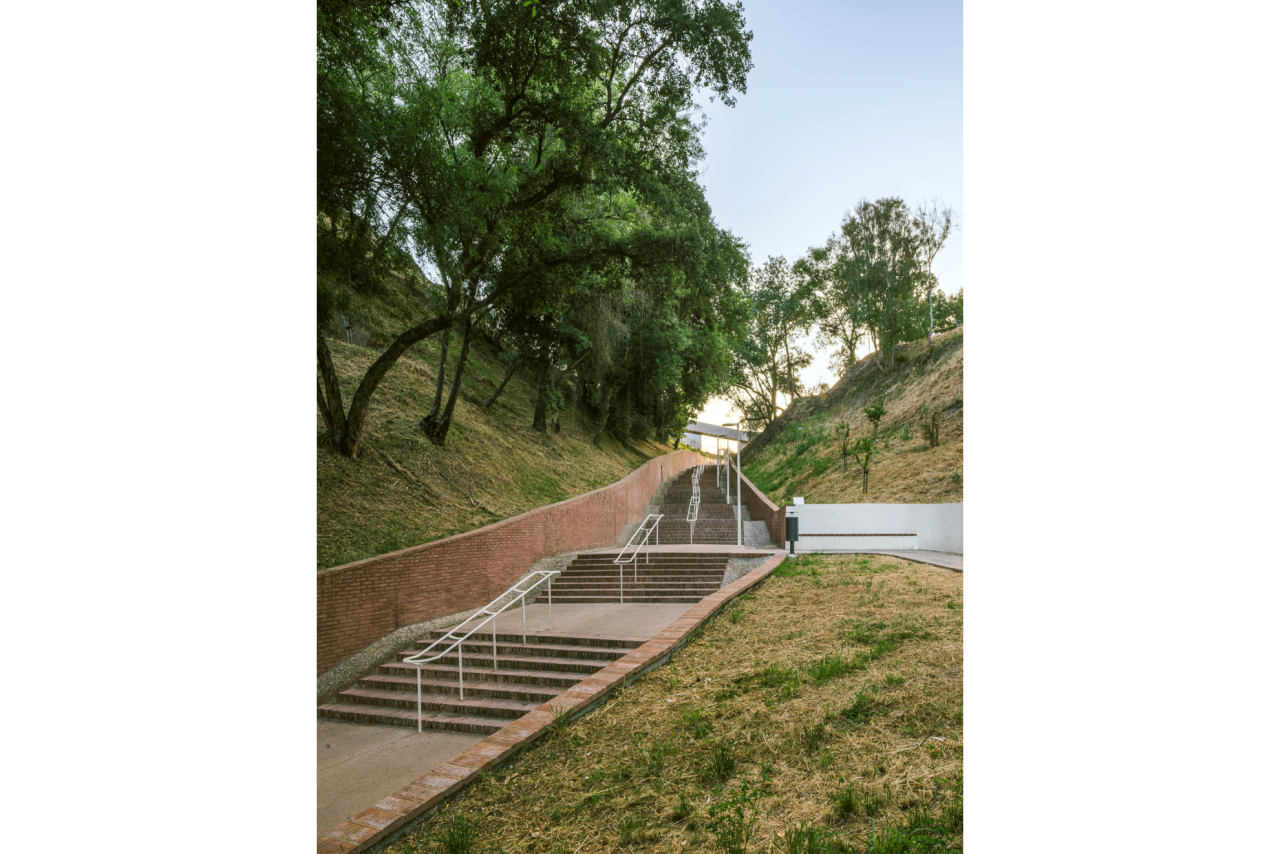
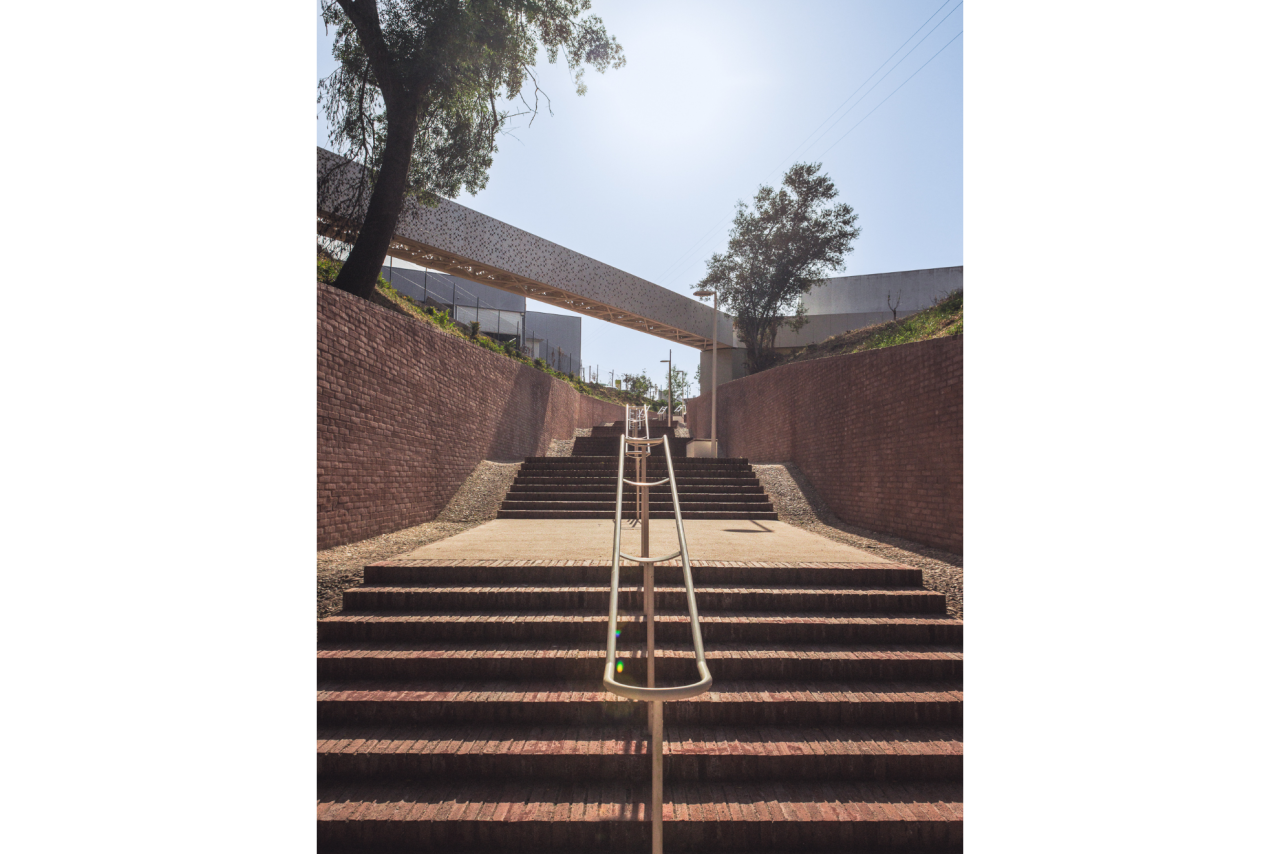
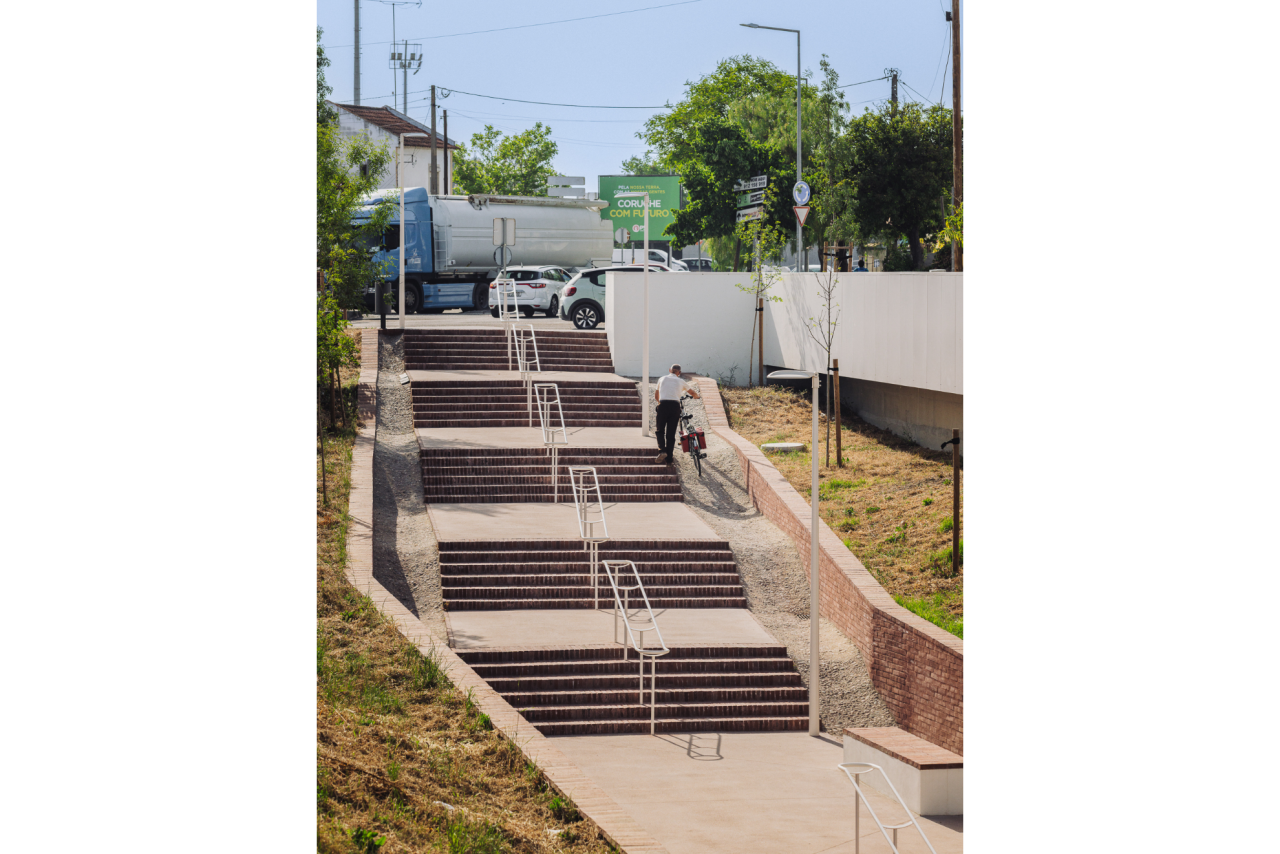
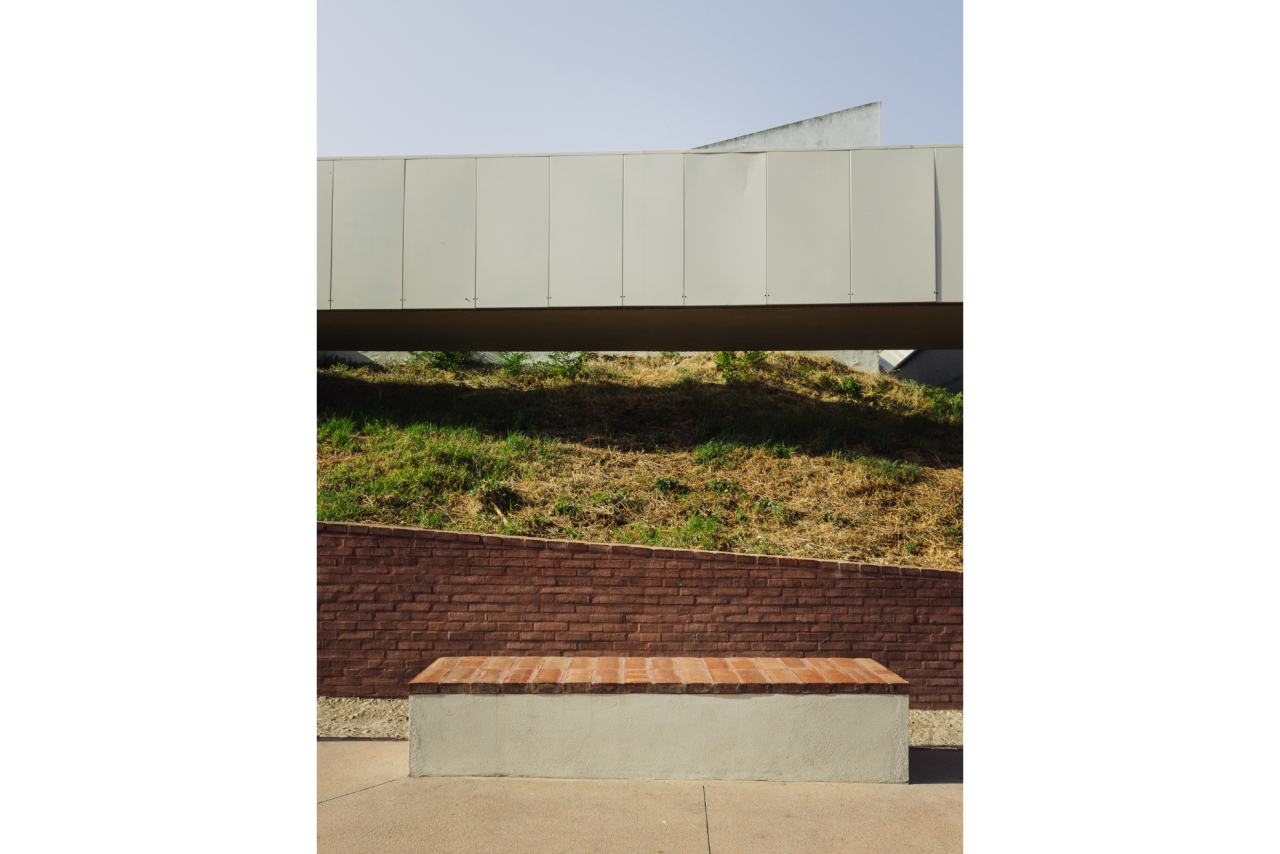
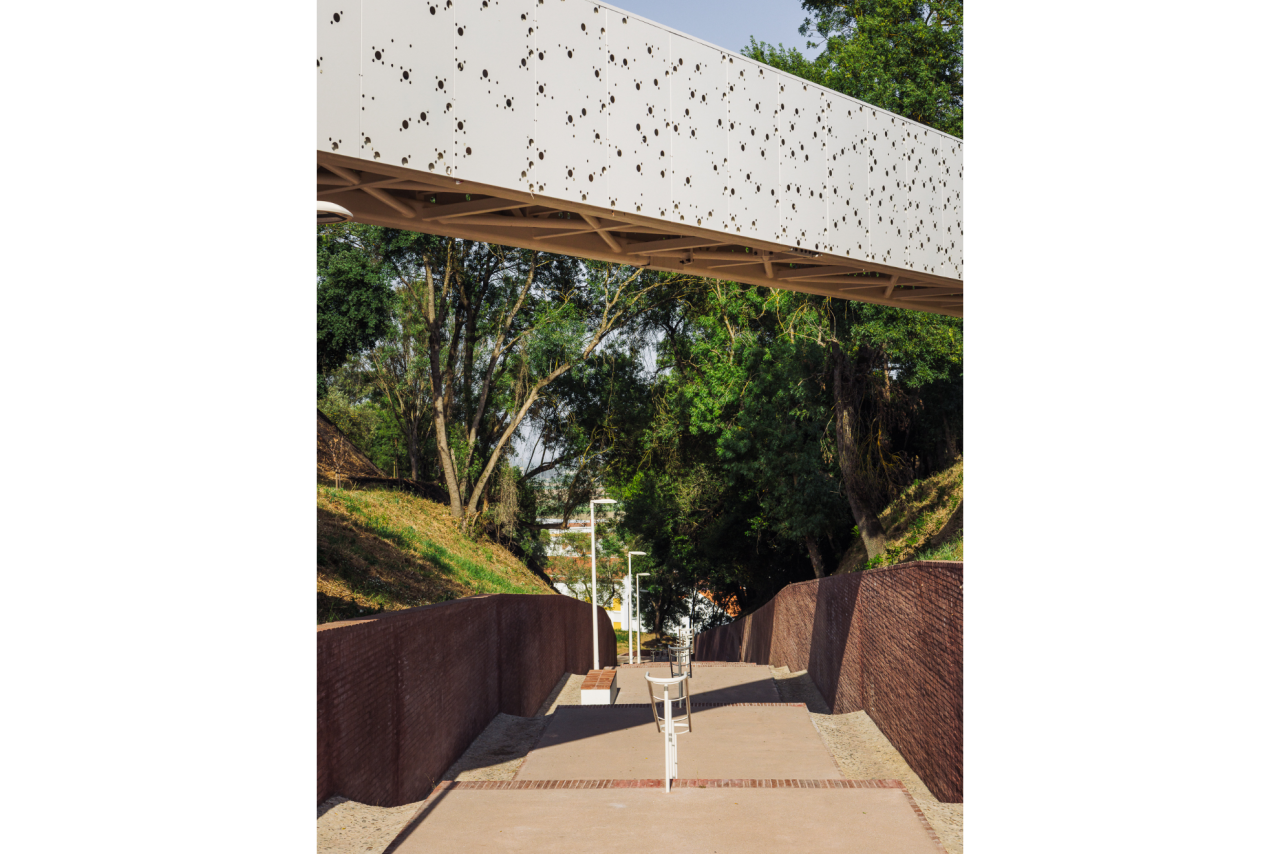
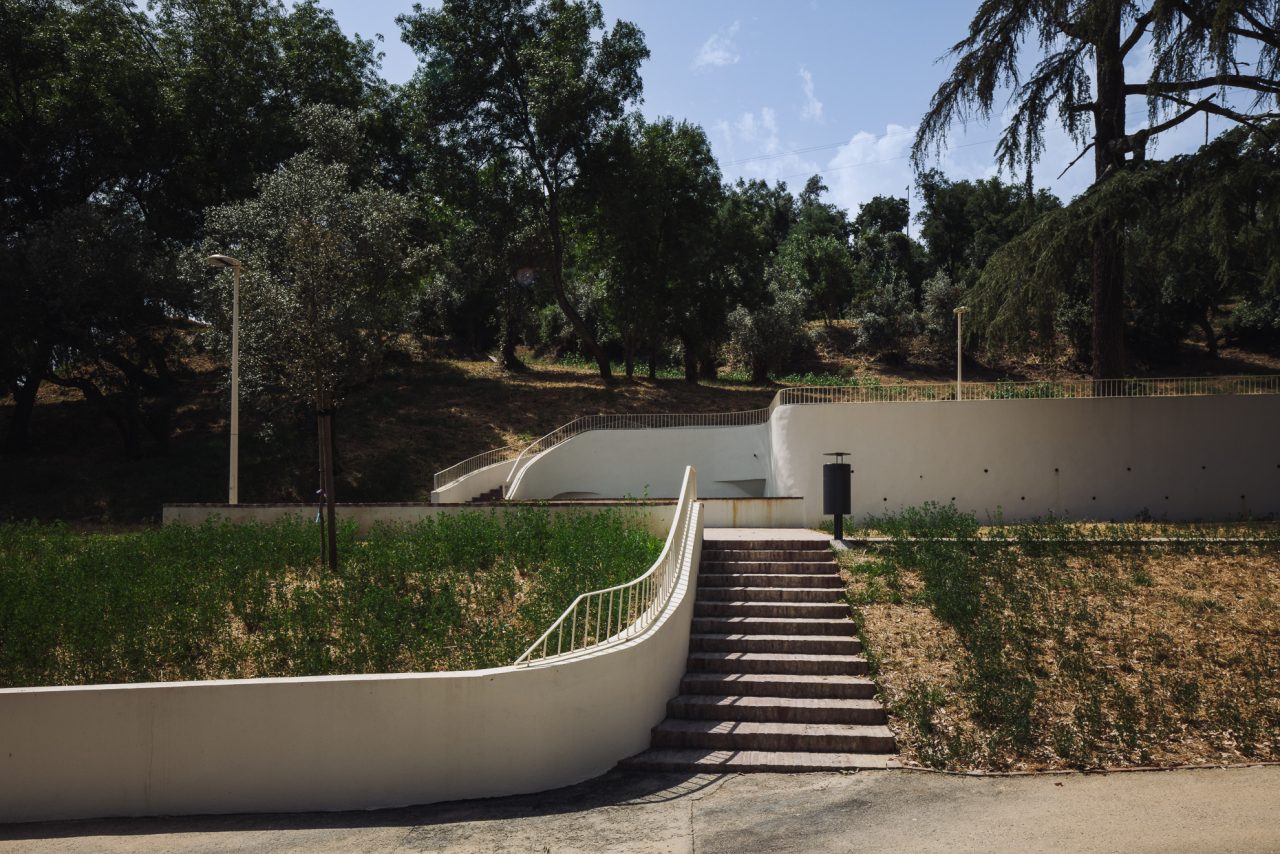
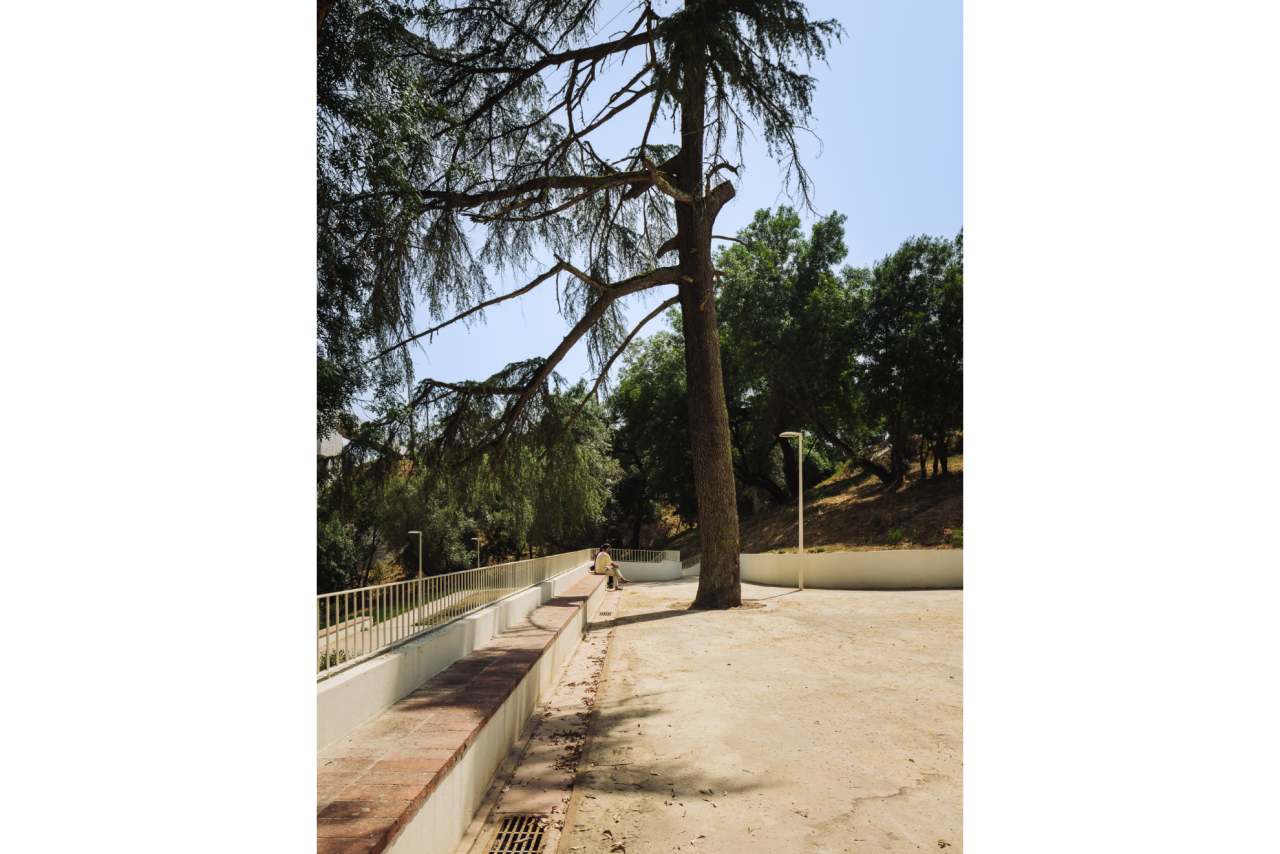
Given the constraints associated with the Calçadinha’s topography and the surrounding slopes, it proved impossible to create a universal route offering a direct path with an acceptable distance compared to the existing one. Therefore, the staircase was rehabilitated to provide greater comfort for pedestrians through the resizing of the flights of steps and the creation of resting areas on the landings along Calçadinha, equipped with urban furniture. An additional access was created using an elevator and a system of walkways, establishing a universal route between Travessa 25 de Abril and Estrada da Lamarosa. The requalification of Quinta do Lago provides conditions for the use of this public space, which preserves the memory of the former estate where the neighborhood of the same name was built. As part of the project, the pre-existing elements were restored — the yard, retaining wall, and the water spring that flows into the tank on the lower terrace — and a network of both universal and non-universal routes was created, linking to the west the Calçadinha staircase, to the south the new square at the beginning of Travessa 25 de Abril, and to the east Rua José Afonso, which defines the upper level of the housing complex.
The planting strategy seeks to restore the balance of the system. Accordingly, two planting zones with different plant compositions are proposed, depending on sun exposure and soil water availability. The proposed vegetation consists mostly of native or regionally characteristic species. Since vegetation plays an important role in the mechanical stabilization of slopes, as well as in erosion control and soil retention, the intervention was carried out with particular care and precision to avoid disturbing the existing balance. Efforts were made to consolidate the existing vegetation, which involves replacing invasive species and planting in areas left without vegetation due to the installation of built structures (walls, walkways, elevator).